How to change halogen downlights to LED
Making the switch from halogen downlights to LED is a wise move. By replacing 10 halogen light bulbs with LEDs an average household can expect to save around AU$650 over 10 years on their electricity bill. LED technology will lower your electricity bill and maintenance costs because it uses very little energy to run effectively. […]

Making the switch from halogen downlights to LED is a wise move.
By replacing ten halogen light bulbs with LEDs, an average household can expect to save around AU$ 650 on their electricity bill over ten years.
LED technology will lower your electricity bill and maintenance costs because it uses very little energy to run effectively.
Your HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning) costs will also be reduced due to the low heat output from LED downlights.
Changing halogen downlights to LED will require an electrician who will assess your current lighting system and then give you a solution that suits your budget and personal style.
In the meantime, you could do your homework so that you can clearly communicate your expectations when the electrician arrives.
Above all, determine what type of halogen downlights you have right now by checking the voltage and connectors.
Bulbs are either low voltage or mains voltage, and the double-pin connectors differ in width to prevent users from switching between bulbs that are too powerful.
What is the difference between mains voltage and low voltage bulbs?
Mains Voltage Light Bulbs
These bulbs have a standard base and require simple installation. Found in residential areas and offices, they’re designed for running voltages of 120, 230 or 240 volts.
G9 Light Bulb

Image from wikimedia by Dmitry G
G9 is the most compact mains voltage halogen bulb and is widely used in small light fittings.
It’s inserted into the fitting with a push thanks to its two flat pins at the bottom, and its wattages range from 20 to 75 watts.
A G9 bulb working effectively reaches temperatures of up to 250°F, giving it a life cycle of 2,000 – 6,000 hours.
Looking at these bulbs without some form of eye protection when they’re switched on is discouraged.
Moreover, touching the bulb even when it’s not hot will lower its lifespan – the grease from your skin and dirt create spots where the glass could begin to crack.
A 3W LED G9 bulb will have the same output as a 20W halogen bulb.
GU10 Light Bulb

Image from wikimedia by Dmitry G
A halogen GU10 is a 240V mains halogen bulb and features a push and twist fitting. It also has a 50mm wide reflector and two studs 10mm apart.
The LED GU10 bulb is a true fit regardless of your fixtures, so replacing your halogen downlights will be easy.
A 5W LED GU10 will have the same output as a 35W halogen bulb.
How do I replace the main voltage halogen downlights with LEDs?
Retrofit your halogen bulbs with compatible low-voltage or mains voltage LEDs. The former will require you to buy an LED driver (LED transformer).
GU10 LED bulbs will work perfectly with your existing halogen fixtures, but you’ll need to ensure that you buy dimmable LEDs if you have a dimmer switch.
If not, go for non-dimmable GU10 bulbs.
Since most GU10s are more than 100mm deep, you might need to get integrated LED downlights, especially if you have a low ceiling void space.
Integrated LED downlights are only 40mm deep due to the built-in LED, with a life expectancy of 7 years.
Their counterparts have a cheaper, replaceable LED which limits their lifespan to 5 years.
Integrated LED downlights effectively control heat dissipation because their fitting is designed around the LED.
Their GU10 LED heat sink is less advanced, directing the heat back into the beam and making it run cool for shorter periods of time.
Low-voltage light bulbs
Low-voltage halogen bulbs have a higher colour temperature, luminous efficiency and longer lifespan. Unfortunately, they can’t function without an external transformer to lower the voltage from 120 or 277 volts to 24, 12 or 6 volts.
The MR (multi-faceted reflector) allows for directional lighting applicable in bicycle headlights, track lighting, as well as recessed ceiling lights in showrooms, hotels and restaurants.
GU4/MR11 Light Bulb
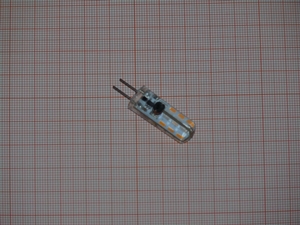
Image from wikimedia by Dmitry G
An MR11 is a 12V halogen bulb with a 35mm wide reflector.
The two sharp pins are 4mm apart, and they allow for a push fit. MR11 bulbs are very small, and as a result, it’s quite common for people to buy the wrong size LED replacements.
Don’t rely on illustrations on the box; ensure that you measure the 35mm LED version before purchase.
GU5.3/MR16 Light Bulb
An MR16 has a push-fit, enabled by the two sharp pins at the bottom that are 5.3mm apart.
This 12V halogen is larger than the MR11 and is popular due to its many designs and beam angles.
It features a 50mm diameter on the reflector and uses a dichroic filter to dissipate heat through the back of the bulb.
MR16 bulbs should be handled with caution as they heat up to at least 260°C. They can cause a fire if they come into contact with combustible material.
How do I replace low-voltage halogen downlights with LEDs?
If you want to retain your low voltage halogen downlights without spending on a transformer, convert them to mains voltage GU10.
The electrician will disconnect the halogen transformer and do some re-wiring, and will then fit GU10 lamp holders and bulbs, which will enable you to plug your downlights into mains power.
Alternatively, you could buy an LED transformer, but first, you’ll have to determine what type you’ve got in your MR16 circuit.
Some circuits have a transformer for each light, while others have a single one for all downlights.
These transformers may either be magnetic or low voltage. If you already have a wire-wound magnetic transformer, you won’t have to buy another one – it will work with LED MR16 bulbs.
An electronic low-voltage transformer needs a minimum amount of voltage to operate and must be replaced. Otherwise, your new LED bulbs will flicker or fail to work.
Make sure that you sum up the individual voltages of your multiple LEDs, then buy a transformer that has the same voltage requirement.
Types of LED Transformers
Constant Current Transformers
Only purchase a constant current transformer if you plan to use it on an individual bulb. Using it in a series will switch off all your downlights whenever your circuit breaks.
A constant current transformer supplies power to LEDs with an existing current-limiting resistor.
It runs on amps (A) or milliamps (mA), varying the voltage throughout the circuit and allowing the current to remain constant.
It not only maintains consistent brightness across all your high-power LEDs but also avoids thermal runaway and premature burnouts.
Constant Voltage Transformers
If you have one transformer for all your downlights, you can buy this driver – it’s perfect for parallel circuits.
You can add as many LEDs as your maximum current allows, and none of the bulbs will go off if the circuit breaks.
Constant voltage transformers power LEDs that have a fixed voltage rating of 24V, 12V, 5V or a higher voltage rating with a maximum current.
There are other alternatives to transitioning to LED. You could use lower-wattage halogen downlights or switch to compact fluorescent lamps.
While this will lower your lighting costs in the short term, it will not take away the headache of proper bulb disposal, overheating and short life span.
